How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed and Treated?
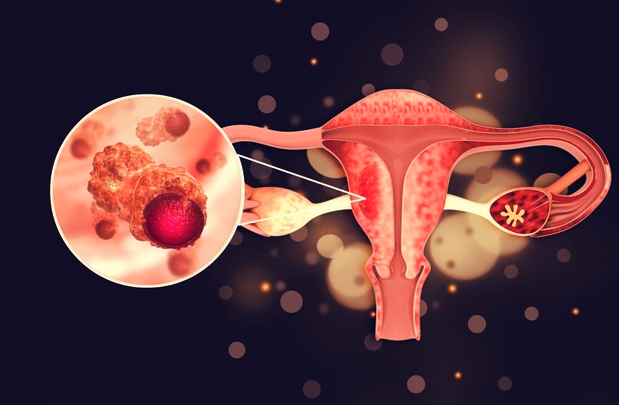
Ovarian cancer is a significant health concern that predominantly develops in epithelial tissue. In its early stages, it often presents no symptoms, making early detection challenging. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as abdominal pain, discomfort, and swelling may arise. Swollen lymph nodes in the groin, armpits, neck, and above the collarbones can also be observed. The diagnostic process for ovarian cancer involves several steps, including physical examinations, imaging tests, blood tests, surgical evaluations, and genetic testing.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Methods for Ovarian Cancer
Physical Examination
A pelvic examination by a specialist is often the first step if ovarian cancer is suspected. This examination checks for abnormal growths, swelling, and enlarged organs. Any irregularities found during this exam can prompt further testing.
Imaging Tests
Advanced imaging techniques are crucial in diagnosing ovarian cancer. Methods such as pelvic ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and positron emission tomography (PET) provide detailed images of the abdomen and pelvis. These images help identify any abnormal growths or tumors.
Blood Tests
Blood tests, particularly those measuring CA-125 levels, are commonly used in diagnosing ovarian cancer. Elevated CA-125 levels can indicate cancer, but this test alone is not definitive. CA-125 levels can be normal in cancer patients and elevated due to other conditions, necessitating the use of additional diagnostic methods.
Surgical Evaluation
Ovarian cancer can sometimes be diagnosed during surgery. Surgeons may remove abnormal growths and cystic structures during this procedure, providing tissue samples for a definitive diagnosis.
Laparoscopy
This minimally invasive surgical procedure involves making a small incision in the abdomen and inserting a camera-equipped tube called a laparoscope. Laparoscopy allows for the removal of biopsy samples and, in some cases, the excision of tumors, aiding in cancer staging and treatment planning.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing involves analyzing blood samples for genetic mutations associated with a higher risk of ovarian cancer. Identifying these genetic changes can guide treatment decisions and inform patients and their families about their cancer risk.
Effective Treatment Options for Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer treatment varies based on the stage and specific characteristics of the disease. Early-stage treatment typically involves surgery, while advanced or high-risk cases may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is the cornerstone of ovarian cancer treatment. The primary goal is to remove all cancerous tissue from the abdomen. If complete removal is not possible, reducing the tumor size to less than 1 cm in diameter is the objective. This approach is essential for managing cancers at all stages, except for end-stage patients.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, also known as cytotoxic or systemic treatment, is crucial in treating ovarian cancer. Most patients receive chemotherapy after surgery to prevent cancer recurrence. This post-surgery chemotherapy is known as adjuvant chemotherapy. Combining surgery with chemotherapy significantly enhances treatment outcomes.
Targeted Therapies
Recent advancements in ovarian cancer treatment include targeted drug therapies. These treatments specifically target cancer cells, disrupting their growth and division. By focusing on cancer cells, targeted therapies offer a more precise approach, potentially reducing side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Hormone Therapy
Some ovarian cancers rely on certain hormones to grow. Hormone therapy aims to block these hormones, slowing or stopping the growth of cancerous tissues. This treatment can be an effective option for hormone-dependent ovarian cancers.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis and Treatment
Ovarian cancer is a severe health issue requiring prompt and effective treatment. If you experience persistent or recurrent symptoms such as abdominal pain, swelling, or discomfort, it is crucial to consult a healthcare specialist. Early diagnosis through comprehensive health screenings and advanced diagnostic methods can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Once diagnosed, your physician will devise a treatment plan tailored to your specific condition. This plan may include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or hormone therapy, depending on the cancer stage and individual factors.
In conclusion, understanding the diagnostic and treatment processes for ovarian cancer is essential for managing this disease. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to early detection, improving the chances of successful treatment and recovery.